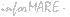 Il World Shipping Council (WSC) ha avanzato una proposta all'International Maritime Organization (IMO) per il miglioramento degli standard di efficienza ambientale delle navi con l'obiettivo di ridurre le emissioni di gas serra. «L'IMO - ha spiegato il presidente e amministratore delegato del WSC, Chris Koch - recentemente ha ottenuto un notevole successo raggiungendo un accordo giuridicamente vincolante a livello globale che ridurrà drasticamente le emissioni di ossidi di azoto e di zolfo e di particolato delle navi in tutto il mondo. È opportuno che, sulla scia di questo successo, l'IMO stabilisca un sistema normativo internazionale che possa ridurre anche le emissioni di gas serra». Il World Shipping Council (WSC) ha avanzato una proposta all'International Maritime Organization (IMO) per il miglioramento degli standard di efficienza ambientale delle navi con l'obiettivo di ridurre le emissioni di gas serra. «L'IMO - ha spiegato il presidente e amministratore delegato del WSC, Chris Koch - recentemente ha ottenuto un notevole successo raggiungendo un accordo giuridicamente vincolante a livello globale che ridurrà drasticamente le emissioni di ossidi di azoto e di zolfo e di particolato delle navi in tutto il mondo. È opportuno che, sulla scia di questo successo, l'IMO stabilisca un sistema normativo internazionale che possa ridurre anche le emissioni di gas serra».-
 La proposta del World Shipping Council, che pubblichiamo di seguito, prevede la definizione di un “Vessel Efficiency System” (VES) che include standard sia per le navi di nuova costruzione che per le navi in esercizio. Le nuove navi - ha rilevato il World Shipping Council - dovrebbero essere soggette a standard di efficienza obbligatori in base ai quali la costruzione delle navi venga effettuata adottando caratteristiche e tecnologie che migliorino ulteriormente l'efficienza energetica delle unità e tali standard dovrebbero essere analoghi a quelli attualmente richiesti in molte nazioni per le automobili e i camion. Inoltre, secondo il WSC, tali standard dovrebbero essere legati nel tempo ad altri standard più rigorosi in considerazione del fatto che lo sviluppo delle tecnologie consentirà ulteriori miglioramenti delle performance ambientali delle navi. La proposta del World Shipping Council, che pubblichiamo di seguito, prevede la definizione di un “Vessel Efficiency System” (VES) che include standard sia per le navi di nuova costruzione che per le navi in esercizio. Le nuove navi - ha rilevato il World Shipping Council - dovrebbero essere soggette a standard di efficienza obbligatori in base ai quali la costruzione delle navi venga effettuata adottando caratteristiche e tecnologie che migliorino ulteriormente l'efficienza energetica delle unità e tali standard dovrebbero essere analoghi a quelli attualmente richiesti in molte nazioni per le automobili e i camion. Inoltre, secondo il WSC, tali standard dovrebbero essere legati nel tempo ad altri standard più rigorosi in considerazione del fatto che lo sviluppo delle tecnologie consentirà ulteriori miglioramenti delle performance ambientali delle navi.-
- La proposta del WSC per le navi già in attività prevede che anch'esse siano oggetto di standard per il miglioramento della loro efficienza ambientale. Tuttavia, dato che per le navi in esercizio è più limitata la possibilità di migliorare tale efficienza - ha spiegato il World Shipping Council - le navi in attività dovrebbero essere oggetto di standard meno rigorosi rispetto a quelli fissati per le nuove costruzioni, anche se - come per queste ultime - anch'essi dovrebbero essere legati a gradi più avanzati di efficienza nel corso del tempo.
-
- Secondo il World Shipping Council, è particolarmente importante stabilire standard di efficienza per le navi in esercizio in considerazione della lunga vita delle navi, che possono operare per 25-30 anni. Infatti il miglioramento delle performance ambientali della flotta in esercizio può contribuire ad una più rapida riduzione delle emissioni di CO2 rispetto ad un sistema di standard applicato alle sole navi di nuova costruzione.
-
- La proposta del WSC prevede che le navi in esercizio che rispettano determinati standard di efficienza ambientale siano esentate dal pagamento di qualsiasi tassa ambientale, mentre le navi in esercizio che non rispettano gli standard dovrebbero essere soggette a una tassazione calcolata sulla base di ciascuna tonnellata di combustibile consumato e sulla base della differenza tra il grado di efficienza della nave e il grado di efficienza fissato dagli standard. La tassa, quindi, dovrebbe essere più elevata per quelle navi che presentano l'efficienza ambientale più bassa.
-
- Il WSC propone che ricavato di tale sistema di tassazione venga utilizzato per costituire un fondo gestito dall'IMO che potrà essere impiegato per finanziare la ricerca nel campo della riduzione delle emissioni inquinanti. Obiettivo di questo sistema è di premiare il miglioramento dell'efficienza ambientale della flotta e di scoraggiare l'impiego di naviglio meno efficiente dal punto di vista del rispetto dell'ambiente.
-
- PREVENTION OF AIR POLLUTION FROM SHIPS
-
- Proposal to Establish a Vessel Efficiency System (VES)
-
- Submitted by the World Shipping Council
-
- SUMMARY
-
|
Executive summary: |
Considering the outcome of the UNFCCC discussions in Copenhagen, as well as recent discussions at the IMO to address GHG emissions from marine shipping, this paper offers views on how to address the challenges to reaching agreement on a global regime and sets forth a proposal to establish a Vessel Efficiency System or VES. |
Strategic Direction: |
7.3 |
High-level Action: |
7.3.1 |
Planned output: |
7.3.1.3 |
Action to be taken: |
Paragraph 27 |
Related documents: |
UNFCCC COP15-/CP.15, MEPC59/4/27, MEPC59/4/30, MEPC59/4/34, MEPC59/4/39, MEPC59/24/Add.1, MEPC59/INF.10., MEPC59/INF.26, MEPC59/INF.27, MEPC.1/Circ. 682 MEPC60/4/4, MEPC60/4/5, MEPC60/4/7, MEPC60/4/XX*, MEPC60/4/XX**, MEPC 60/4/XX***, |
|
- Introduction
-
- This document is submitted in accordance with paragraph 4.10.5 of the IMO guidelines on method of work, MSC-MEPC.1/Circ.2. In light of the outcome of the 15th Conference of the Parties held in Copenhagen (COP15) and the discussion that occurred in Copenhagen concerning bunkers for international shipping, this paper offers views on how to build consensus to address the challenges in development of a broadly accepted framework and introduces a proposal to establish a Vessel Efficiency System (VES) within the IMO.
- During COP15, the parties discussed the issue of whether specific emission reduction targets or emission caps should be established for international shipping. The parties at COP15 did not agree to establish targets applicable to GHG emissions from international aviation or international maritime traffic. Although COP 15 reached no agreement on how emissions from shipping or aviation should be regulated, we believe the IMO, as the appropriate body, should continue to move forward with development of a global agreement for maritime shipping that will significantly improve energy efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions in a manner that may be deemed acceptable by a broad range of governments and other interested parties.
- As discussed in MEPC 60/4/XX, the World Shipping Council (WSC) believes that it is important to consider this question in the context of how sources of carbon emissions from transportation in general have been regulated around the world. We also believe it is important for the Committee to proceed along a path that has the potential to overcome some of the significant conceptual barriers that have arisen in trying to articulate how the Member States could move forward with a global agreement that is relatively simple to administer and implement, improves the industry's environmental performance, is equitable, and can be broadly supported.
- Discussion of a global agreement to date has largely centered on a discussion of “market based initiatives” that has tended to characterize the choice as being between two concepts - the fund as initially proposed and later modified by Denmark, or an open emissions trading system as proposed by Norway, Germany, and France. Both concepts have merits, but it is also clear that numerous parties have serious concerns with proceeding with development of a global agreement that is based on either system.
- More recently in the debate, both Japan and the United States offered proposals that seek to focus on and reward vessel efficiency. An efficiency-based approach is fully consistent with the environmental regulatory models employed by numerous governments across the globe. Such an approach can be structured to be consistent with commercial market requirements, because business decisions can then be made on a regime that assigns predictable costs to achieving a given standard. Furthermore, the approach is not prescriptive because the ship owner or operator can choose the action or actions that are most appropriate for meeting the standards articulated in the agreement.
- The IMO can establish an effective carbon regime for shipping by developing a rigorous global system that fosters and rewards enhanced vessel efficiency. As noted previously, proposals with this objective have been made by Japan (through rebates of moneys paid under a levy system) and the United States (through vessel efficiency standards and trading in vessel efficiency credits), and we encourage the IMO to focus on improving vessel efficiency. Indeed, we believe that the most promising path forward at this time is to pursue a regime that focuses on improved fuel and carbon efficiency across the fleet. Improved energy efficiency with its consequent reduction in CO2 emissions is a goal that has been embraced broadly by numerous governments across the globe - both Annex I and Non-Annex I governments. Consequently, a simple regime that focuses on improving the efficiency of the world's fleet would produce quantifiable and significant improvements, while also providing a path that avoids many of the political obstacles that have hampered efforts to date.
- An efficiency based approach does not begin from the premise that the world's fleet is inefficient. The fleet is already efficient, but further improvement will lead to reduced carbon emissions and lower fuel bills. The later will become especially relevant as many energy consultants have forecasted significant increases in the costs of fuel (both light and heavy fuel oils) in coming years.
- In an effort to contribute to the consideration of measures that could incentivize enhanced vessel efficiency of the world's fleet and thus reduce global carbon emissions from shipping, the World Shipping Council offers the following market-based concept for consideration by the Committee.
- The Proposal
-
- Drawing on the most positive aspects of the proposals made to date, the World Shipping Council offers a market-based proposal for consideration by the Committee. The proposal is based on:
a) establishing efficiency design standards or targets for both new and existing vessels in the fleet where calculation of an EEDI baseline is deemed feasible,
b) establishing mandatory efficiency standards applicable to new builds built after a particular year with subsequent standards established through successive tiers (e.g., X% by year 20XX, Y% by year 20XY),
c) establishing different efficiency standards (less stringent that those applicable to new builds) that apply to the existing fleet after a given year to be determined by the parties,
d) the assessment of charges (based on fuel consumption) for those existing vessels failing to meet the applicable standard established for existing vessels, and
e) the establishment of a fund populated by those charges collected.
It is important to note that under this proposal fuel charges would apply only if a vessel fails to meet the applicable efficiency standard and the specific charge would vary depending upon how far the vessel's efficiency (as measured by the EEDI) falls short of the applicable standard.
- The purpose of combining vessel design efficiency with the fund concept is to:
a) produce an enhanced environmental result;
b) address the criticisms that the present proposal to establish a fund through fees on all bunkers sold would be an international commodity tax, and that such an approach would have limited impact on improving carbon efficiency across the world's fleet;
c) provide greater financial incentive to vessel operators that invest in efficiency improvement; and
d) discourage the long-term operation of the most inefficient vessels.
- Under this proposal, the charge assessed for each ton of fuel purchased1 would apply only to vessels failing to meet the efficiency design standard mandated
|
1 As with the Danish proposal, each ton of purchased fuel is assumed to be consumed with a consequent contribution to the global carbon inventory.
|
|
- For those ships subject to the charge, the charge would be assessed upon each ton of fuel purchased, but the specific charge per ton of fuel would vary depending upon how “far” the vessel fails the efficiency standard established in the treaty. As such, the relative cost per ton is less for those ships that miss the standard by a smaller margin. In contrast, the least efficient ships of a given class and size would pay the highest charge.
- How would this option work?
- All vessels classes, both new and existing, that have been included under the EEDI scheme, are assigned a vessel efficiency score using the IMO Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) by the Administration or class organizations authorized by the Flag State.
- Vessels would be grouped by class and by size so that one may determine the relative efficiency of each vessel within the group. For example, all VLCC tankers of a given size range would constitute a particular group; all container vessels with a nominal TEU capacity of X to Y would constitute a
|
2 The exact parameters of the groups would have to be decided by IMO (e.g., for container ships, every 2,000 TEU of capacity might be a separate group). This memorandum does not propose specific vessel size definitions for such groupings, as it only seeks to propose the option in conceptual form at this time.
|
|
- New Builds vs. Existing Vessels: As noted earlier, under the proposed VES, new builds would be subject to more aggressive efficiency improvements, while existing ships would be subject to more modest improvements consistent with the more limited options available for improved efficiency among existing ships. Both the new build and existing vessel efficiency standards would be subject to tiered improvements established at levels and intervals deemed appropriate by the parties in light of the relevant technical options and market implications.
- Consistent with work already underway in the IMO GHG WG, baselines would be calculated for each of the respective vessel classes with breakouts by vessel size as appropriate. Once the average for the various vessel groupings by class and size are determined, governments would establish within the IMO treaty a specific improvement in the average efficiency of the world's fleet (e.g., X% improvement in average vessel efficiency when compared to today's average) and thereby create a specific target for efficiency improvement from new vessels of X%. A similar process, with less ambitious improvements in efficiency would also be undertaken for the existing fleet.
- Determining EEDI Values for Existing Vessels: Each vessel covered by the Vessel Efficiency System (i.e. those vessel classes where an EEDI baseline has been established and whose tonnage is above the established coverage threshold) is assigned a specific EEDI value using the formula developed by the IMO. Specific data elements in the EEDI formula, such as sfc that may not already be certified for some vessels, would be subject to default values to be agreed upon by the parties.
- Each vessel in the existing fleet that is covered by the scheme would then be judged against a requirement to reduce its emissions by X% below the average efficiency (likely referred to as a baseline) for the specific vessel class and size that a given vessel falls within (e.g., containership of a 2500-4500 TEU size).
It could do so in two ways:
- by the actual design index for that vessel being technically as efficient or more efficient than the required design index of other vessels of the same class and size, and
- to the extent that the vessel is less efficient than the target value, the vessel would pay a variable charge equal to some $ amount to be determined per ton of fuel used.
- If an owner or operator were to make technical improvements to its vessel that improves the efficiency of the vessel, the vessel should be recertified by a recognized organisation and assigned a new EEDI value. Recognizing this, improvements in a vessel's design efficiency, including speed reduction through de-rating of propulsion engine(s), would be formally recognized under the system and would be rewarded through two mechanisms: 1) a lower fuel charge (if any) proportionate to the improved efficiency of the vessel, as well as, 2) lower fuel consumption.
- The least efficient vessels in each group (organized by class and size) would experience higher operating costs through higher per-unit fuel costs and higher consumption associated with the lower efficiency of the vessel.
- Like the Danish proposal, such a system would generate funds for an IMO administered “fund;” however, this approach would also financially reward those ships that meet the specified efficiency standards and create an incentive to improve or retire the least efficient vessels within a given class and size grouping.
|
3 The use and percentage of funds devoted to a given purpose is an independent variable that would be addressed by governments at the IMO.
|
|
- The fuel charge would be collected through registered fuel suppliers or by the ship directly as proposed in MEPC60/4/7, with funds transferred to the International Fund Administrator. Use of the funds would be determined by the parties, but WSC proposes that some significant portion of the funds be dedicated to research and development projects targeted at increasing the energy efficiency of the world's fleet.3
- Attached at the end of this submittal is Appendix A, which provides a detailed, step by step explanation of how the Vessel Efficiency System (VES) proposal would work and how the variable fuel charge would be calculated for a specific vessel. While an initial impression may be that the formula in the Appendix seems complicated, we believe that it is an equitable mechanism for motivating improved efficiency across the fleet.
- A fuel charge for vessels that fall short of the required efficiency design standard could also be set at a flat rate per ton of fuel as an alternative approach if the variable fuel charge were determined to be too complicated. This approach is simpler, but is less equitable in the magnitude of the incentive and reward for greater vessel efficiency.
- Advantages Associated with the VES Proposal:
-
- Debate within the IMO and the UNFCCC to date has been hampered by concerns regarding: 1) development constraints on Non-Annex I countries, 2) major uncertainties concerning the predictability and operation of certain systems, and 3) the long-term viability of approaches that rely largely on “offsets” outside the maritime sector, and on the imposition of fees viewed by some governments as an international commodity tax. The VES proposal seeks to draw on elements of many of the proposals submitted to date and offers a potential path forward that focuses on definitive fleet improvements in both the near and long-term. A short list of advantages that could be associated with the proposal follows:
- The VES Proposal would result in predictable, quantitative, and measurable improvements across the maritime fleet.
- This approach would not assess a charge on fuel purchased by ships that comply with the applicable IMO efficiency standard.
- For vessels that fail to meet the standard, the variable or “sliding scale” charge would create a direct market incentive to vessel operators based on the relative efficiency of the vessel.
- This approach would encourage operators of the least efficient vessels to improve the efficiency of the vessel or retire the vessel if the operating cost is higher than other business alternatives.
- This approach would avoid inappropriate comparison of vessels within a given class that serve very different purposes and possess very different efficiencies related, in large measure, to substantial differences in size.
- This approach would provide a source of money to an “IMO GHG Fund”.
- The VES does not constrain or otherwise disadvantage non-Annex I countries since the system is not dependent upon financial markets or third-party brokers. The VES may also be structured to exempt smaller vessels whose owners may face more significant challenges to improving vessel efficiency - especially relevant for small operators in developing countries.
- This approach would address the environmental criticism of the current fund proposal that the fuel charge is an added cost that would be paid across the shipping sector, but would fail to change industry behavior, vessel efficiency, or significantly reduce carbon emissions from ships.
- By making the fuel charge vary by relative efficiency and by not imposing the charge on vessels that meet the established goal, this approach would effectively eliminate the argument that the system constitutes an international commodity tax on marine fuel sales.
- Three appendices follow: Appendix A provides further detail on how the proposed VES would function, including how specific fuel charges would be calculated for vessels failing to meet the relevant efficiency standard; Appendix B addresses elements identified in the work plan developed and approved at MEPC 59; and, Appendix C outlines how the proposal satisfies the nine IMO principles agreed earlier by the Committee.
- Action requested of the Committee:
-
- The Committee is invited to consider the information in this document and take action as appropriate.
- APPENDIX A
-
- Vessel Efficiency System (VES)
-
- Calculation of variable fuel charge based on vessel efficiency
-
- The primary elements of the Vessel Efficiency System (VES) concept, as well as the method to be employed in calculating the variable fuel charge, are as follows:
-
- Calculate a “baseline” design index for all ships included in the scheme using the IMO Design Index, grouped by vessel class and size.
- Governments would establish within the treaty a specific improvement in the average efficiency of the world's fleet (e.g., an X% improvement in average vessel efficiency when compared to today's average) and thereby create a specific target for CO2 emission improvement from ships of X%. These improvements could be established in steps or tiers, so that X% improvement is required by a defined date and X+% is required by a subsequent defined date. The efficiency standards for new builds would also be more aggressive than those established for the existing fleet.
- It is proposed that each group of vessels (defined by class and size) be subject to the same percentile improvement over the group average.
- Each individual vessel would then be judged against a requirement that its emissions should be X% below the average efficiency (likely referred to as a baseline) for the specific vessel class and size that a given ship falls within (e.g., containerships of a 2500-4500 TEU size).
- A newly built vessel must be built to satisfy the EEDI value required of new builds at the time of construction.
- An existing vessel could meet this requirement by:
A) Possessing a design index value that meets or exceeds the stipulated standard;
B) Through technical efficiency improvements that allow its efficiency design index to be lowered and certified;
C) By payment of a variable fuel charge dedicated to an IMO fund, or
D) By a combination of options B and C.
- Each vessel would then assess the following:
A) Can the vessel improve its design index value through technical improvements? If yes, then improvements will lessen the fees assessed relative to the degree of improvement in the vessel's efficiency. If the owner is able to make technical modifications that totally meet the target efficiency value and are so certified, then no fuel charge would apply.
B) Once the vessel has made the technical improvements that are deemed feasible, the fuel charge to be paid would be determined by the extent that the ship (after technical modifications) is less efficient than the target value (i.e., 1-X% of the average design index for vessels of that class and size). The ship would pay a fuel charge equal to some $ amount to be determined per ton of fuel used.
- The amount of the fuel charge (FC) that a vessel would pay to the fund would be determined by a formula
|
4The above examples are provided strictly for illustrative purposes and are not intended to suggest what % improvement would be applicable to the fleet.
|
|
FC = (Rtarget - (1 -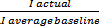 )) x (fuel charge per ton of fuel or $Y) x (tons of fuel consumed). For example4, if the percentage improvement (Rtarget) were determined by the IMO to be 10%, then the fuel charge (FC) would be equal to )) x (fuel charge per ton of fuel or $Y) x (tons of fuel consumed). For example4, if the percentage improvement (Rtarget) were determined by the IMO to be 10%, then the fuel charge (FC) would be equal to
.10 - (1 - 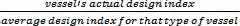 ) )
- Thus, assuming, solely for the purpose of illustration, that governments at the IMO decided that the charge per ton of fuel ($Y) is $90/ton, and vessels should be held to a standard to improve efficiency by 10% by a particular year, and the example vessel burns 50,000 tons per year, then -
a. A vessel
|
6 In this example, the average efficiency (or baseline) for a particular vessel group is 16 grams per ton mile.
|
|
b. A vessel whose design is 5% more efficient than average would pay less per ton, or ($Y) (tons of fuel burned) (.10 - (1- ( )6 or in this example, ($90/ton) (50,000 tons of fuel burned) (.05) = $225,000 for the year. )6 or in this example, ($90/ton) (50,000 tons of fuel burned) (.05) = $225,000 for the year.
c. A vessel whose design index was 10% more efficient than the average vessel in a given group of vessels of the same class and similar size would pay no fee because it has fully achieved the objective or Rtarget .
d. A vessel whose design is 10% less efficient than the average vessel of that type would pay more per ton, or ($Y) (tons of fuel burned) (.10 - (1-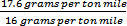 ), or in this example ($90/ton) (50,000 tons of fuel burned) (.20) = $900,000 for the year. ), or in this example ($90/ton) (50,000 tons of fuel burned) (.20) = $900,000 for the year.
- The above formula and examples explain how the variability of the fuel charge would operate depending on the vessel's efficiency. The actual amount or quantum of the fuel charge paid to the Fund would be determined by the relative efficiency of the vessel compared to the vessel efficiency standard (EEDI) established by the IMO as well as the level of the base charge that would be established per ton of fuel.
- APPENDIX B
-
- MEPC Work plan Considerations - Vessel Efficiency System (VES)
-
- Feasibility of the System
-
- The proposed Vessel Efficiency System or VES is focused on using efficiency formulas that have been under development and review at the IMO for some time. While we expect the EEDI will be further refined with experience, the formula does represent a mechanism for evaluating the inherent design efficiency of vessels, both individually and on a comparative basis.
- Robustness of the System
-
- The proposed Vessel Efficiency System or VES is one of the more simple market-based proposals tabled for consideration at the IMO. It also relies on technical formulas that have been developed and debated over multiple years within the IMO. Efficiency values can be derived through quantitative methods agreed upon by the parties and certified by Recognized Organizations.
- Funds generated under the proposal could be collected and paid through the same mechanisms outlined in the Danish proposal. Where fuel charges are applicable, such payments may be made through registered fuel suppliers or through direct payment by the vessel or its representative.
- Costs associated with the operation of the VES would be predictable so that companies may plan operations and otherwise make investments within a system where costs and market alternatives are clearly defined and known in advance. Vessels complying with the relevant efficiency standards would incur no additional costs beyond those investments made in achieving the necessary standards. Costs applicable to vessels failing to meet the relevant standards would also be predictable over time so that the owner and operator can assess whether operation of the vessel is profitable and under what conditions.
- Environmental Effectiveness of the system
-
- Because the proposed system is focused on achieving efficiency improvements across the world's fleet, the proposed VES would produce quantifiable improvements in efficiency and reductions in CO2 emissions for the world's fleet. As such, the VES proposal offers a mechanism for actual improvements within the world's fleet. Unlike some proposals, it does not rely on “offsets” in other sectors to achieve environmental benefits. Instead most environmental benefits can be achieved within the sector itself. This in turn, has at least three notable advantages. First, by achieving reductions within the sector itself, the VES proposal would directly contribute to the improved carbon efficiency and sustainability of the maritime transport sector. Secondly, progressive improvements in efficiency across the fleet will ensure that maritime shipping continues to be the most carbon-efficient form of transportation. Third, the system should be politically sustainable because specific environmental targets and environmental results can be achieved within the sector itself, and do not require offsets from other industrial sectors.
- Administrative burdens and costs of the system
-
- Administrative costs and burdens associated with the system would be similar to those encountered for the Danish GHG Fund if fuel suppliers are used as a conduit for the collection of funds. Should payment of the necessary funds be limited to vessels, then the respective universe of administrative burdens associated with monies in the system would be limited to only those vessels failing to meet the established efficiency standard.
- Administrative burdens and costs associated with certification and modification of a vessel's efficiency score would follow the same norms established in the industry for the certification and recertification of other vessel modifications where certification by recognized organizations or the respective Administration is required. These costs would be greater for vessels that made numerous minor technical improvements to a vessel over a period with certification of each modification. We believe that this scenario will be limited as most vessel owners and operators would logically choose to limit recertification to a group of technical modifications made during a single dry-docking session or to a group of modifications made in a short time frame.
- Impact on international shipping and the maritime sectors of developing countries
-
- Under the VES Proposal, transoceanic and coastal shipping would maintain its leadership as the most carbon efficient mode of transportation. Improvements in vessel efficiency for both new and existing vessels would be rewarded directly in the Vessel Efficiency System and through savings in future fuel costs.
- Large, transoceanic vessels that are registered in developing countries or that serve developing countries' commerce should be able to operate under the VES with no competitive disadvantage. To the extent it is found that smaller vessels are engaged in local or regional trade in developing countries would have a difficulty with compliance with the VES, such an effect could be mitigated by establishing the applicable threshold in gross tonnage at a level designed to exempt or otherwise mitigate adverse impacts on smaller vessels operating in developing countries.
- APPENDIX C
-
- Conformance with the Nine IMO Principles
Vessel Efficiency System (VES)-
- Adherence with the nine fundamental IMO principles
-
- Consistent with decisions made by this Committee, IMO GHG instruments should meet all of the nine fundamental IMO principles for future regulation on GHG emissions from international shipping. A review of the nine IMO principles follows:
-
- Principle 1: Effective in contributing to the reduction of global greenhouse gas emissions
-
- 1. The proposed Vessel Efficiency System (VES) would provide a mechanism that would reduce global greenhouse gas emissions through improved fuel efficiency and reduced CO2 emissions in the fleet. The fund would also provide a mechanism for funding research and development as well as mitigation projects consistent with decisions taken by the parties.
-
- 2. The VES is designed to drive measurable improvements in both new and existing ships. As a result, the VES system is attractive from both an environmental and public policy standpoint because the approach produces real and quantifiable reductions within the world's fleet itself. The VES does not rely on other sectors to achieve reductions through “offsets”. Rather, carbon efficiency in the sector - which is already superior to other transportation modes - will continue to improve, ensuring that maritime transportation continues to be the most fuel and carbon efficient transportation mode into the future.
-
- 3. The fund established under the VES proposal also provides a second mechanism for reductions both within and outside the shipping sector. Improved carbon efficiency would be enhanced through specific marine efficiency research and development efforts while monies would also be available for mitigation projects outside the maritime sector.
-
- Principle 2: Binding and equally applicable to all flag States in order to avoid evasion
-
- 4. The proposed VES is applicable to all flag states to ensure a level playing field for maritime transport.
-
- Principle 3: Cost-effective
-
- 8 The VES imposes minimal administration costs due to the system's simplicity and the fact that it utilizes technical formulas already developed by the organization, allows owners and operators flexibility in how to achieve a given standard, and by its very nature, ensures that vessel owners and operators will enjoy the benefit of lower fuel bills for the life of the vessel as improved fuel and carbon efficiency are explicit goals of the proposed system.
-
- Principle 4: Able to limit - or at least - effectively minimize competitive distortion
-
- 9 Subject to a tonnage threshold to be determined by the parties, all ships in international trade would be subject to the VES. As such, the standards are applied uniformly across the world's fleet with minimal competitive distortions.
-
- 10 The competitive position of the most efficient ships is enhanced in the system while the cost of operating the most inefficient ships is increased. Both factors provide a direct market incentive to continually improve fleet efficiency.
-
- Principle 5: Based on sustainable environmental development without restricting global trade and growth
-
- 11 The Vessel Efficiency System (VES) would not penalize or constrain growth in global trade. To the contrary, efficiency improvements to be realized across the fleet through application of the VES would ensure that both transoceanic and coastal shipping remains the most carbon-efficient transportation mode in the world and that further growth and development of the industry is sustainable over the long-term. Other proposals are designed to generate considerable sums of monies to facilitate offsets and other mitigation efforts external to the sector with limited effect on driving improved efficiency in the fleet. The VES ensures that real and quantifiable improvements in efficiency will be achieved across the maritime sector. The IMO GHG Fund will also provide a vehicle for helping broader sustainable development goals to address the GHG issue both within and outside the maritime sector.
-
- Principle 6: Goal-based approach that is not prescriptive in nature
-
- 12 The system does not require vessel owners to limit operations or total fuel consumption. Rather, the system establishes efficiency standards where the vessel owner and operator may choose what modifications or methods are most appropriate to meet the applicable standard. Furthermore, market considerations for specific trades will influence the decision of a given owner and operator as to whether it makes sense to operate a vessel that is less efficient than the required standard.
-
- Principle 7: Supportive of promoting and facilitating technical innovation and R&D in the entire shipping sector
-
- 13 The VES provides a direct mechanism and global framework for achieving quantifiable improvements across the global fleet. The VES would directly stimulate innovation in both new builds and the existing fleet as operators seek to meet or exceed efficiency targets stipulated in the VES. In addition, the WSC recommends that a substantial portion of funds generated through the VES are to be invested in R&D projects to accelerate improved carbon efficiency in the fleet.
-
- Principle 8: Facilitates new technologies in the field of energy efficiency
-
- 14 The VES provides explicit mechanisms for directly improving energy efficiency in the maritime sector. The fund established under the VES also provides for investment in leading energy efficiency technologies and projects outside the maritime sector.
-
- Principle 9: Practical, transparent, fraud free, and easy to administer
-
- 15 The practicality of the proposed VES is significant since it directly motivates improvements in the maritime fleet that will lead to significant environmental results while also enabling vessel owners and operators to enjoy improved efficiency in a business setting that anticipates significant increase in the cost of fuel across the globe.
-
- 16 The proposed system is fully transparent and predictable since the cost of operating a vessel that fails to meet a given efficiency standard can be calculated in advance with a consequent benefit of allowing the relevant business interests to plan how they will modify their existing fleet, where deployments of specific vessels are most profitable, and when retirement of the least efficient assets are warranted in a given market.
-
- 17 Transparency is also enhanced under the VES since vessels under the system would all possess EEDI values that can be verified by the Flag State Administrations, Port State Control Authorities, and recognized classification societies. Moreover, administration of the VES would be reasonably straight forward because administrative responsibilities fall into two basic categories: 1) certification and recertification of vessel EEDI values consistent with appropriate efficiency modifications made to the ship, and 2) the collection and disbursement of monies collected via the VES fund.
|